What are autoimmune diseases?
 The immune system is a complex network of cells and other molecules. The normal role of the immune system is to protect the body and treat infections caused by bacteria, viruses and other microbes that invade the body. When someone suffers from an autoimmune disease, his immune system erroneously attacks his own body, targeting his cells, tissues and organs, often by creating autoantibodies. Accumulation of cells and other immune system molecules at a body site that is attacked, either naturally in the context of an infection or mistakenly in an autoimmune disease, is widely referred to as inflammation.
The immune system is a complex network of cells and other molecules. The normal role of the immune system is to protect the body and treat infections caused by bacteria, viruses and other microbes that invade the body. When someone suffers from an autoimmune disease, his immune system erroneously attacks his own body, targeting his cells, tissues and organs, often by creating autoantibodies. Accumulation of cells and other immune system molecules at a body site that is attacked, either naturally in the context of an infection or mistakenly in an autoimmune disease, is widely referred to as inflammation.
There are many different autoimmune diseases, each of which can affect the organism in different ways. For example, the autoimmune reaction is directed against the brain in Plaque Sclerosis and against the intestine in ulcerative colitis. In other autoimmune diseases, such as Systemic Lupus, the affected tissues and organs may vary from patient to patient as there is a wide range of organ and system attack (so called multi-systemic disease). A wolf patient may have skin and joint damage while someone else has kidney and lung involvement. Finally, damage caused by the immune system to certain tissues may be permanent or transient.
Who are affected by autoimmune diseases?
Although these diseases are not very common, millions of people are infected around the world. Despite the general perception that rheumatic diseases are diseases of the third age, due to the increased occurrence of various degenerative ("age" as we say) conditions such as osteoarthritis, pure autoimmune diseases are usually diseases of young age, and Especially of women of childbearing age. Also, infants, young children and adolescents may be infected with a low rate, with rheumatology which is called rheumatology.
Are autoimmune diseases transmissible?
These diseases are not transmitted to other people like infections, they do not stick to each other. They are also not related to AIDS, nor are they a form of cancer.
Are autoimmune diseases hereditary?
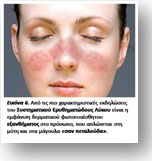 Genes that people inherit from their parents contribute to the predisposition for the occurrence of a disease, not just autoimmune. However, other environmental factors, such as smoking, Rheumatoid Arthritis, intense exposure to sunlight for Wolf, etc. (Figure 6) need to be shown. In addition, some members of the same family may have the same group of "predisposing" genes but have different autoimmune diseases. For example, a first cousin may have Whip, another Multiple Sclerosis, and one of their mothers Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Genes that people inherit from their parents contribute to the predisposition for the occurrence of a disease, not just autoimmune. However, other environmental factors, such as smoking, Rheumatoid Arthritis, intense exposure to sunlight for Wolf, etc. (Figure 6) need to be shown. In addition, some members of the same family may have the same group of "predisposing" genes but have different autoimmune diseases. For example, a first cousin may have Whip, another Multiple Sclerosis, and one of their mothers Rheumatoid Arthritis.
What factors can affect the appearance of an autoimmune disease?
It is well known that some autoimmune diseases first appear or worsen by some stimuli, eg after a viral infection, a strong emotional stress, etc. In Systemic Erectile Dysfunction, eg continuous exposure to bright sunlight can cause predisposed individuals to manifest Disease, while in already afflicted patients,
May cause symptoms to worsen both from the skin and from the internal organs affected. Another factor that has recently been shown to be incriminating for rheumatoid arthritis is smoking, although the mechanism of damage is not yet fully understood. Other factors that also seem to affect the onset or worsening of autoimmune diseases are intense anxiety, female hormones (hence more often in women), pregnancy.
What are autoimmune diseases and which of them is the specialty of rheumatology?
Based mainly on the target organ or its particular mechanism of attack, autoimmune diseases include a variety of diseases with which various specialties are involved. Indicatively, we refer to the contested body:
| Nervous system | Multiple Sclerosis, Heavy Myasthenia, Guillain-Barre Syndrome |
| Hematopoietic system | Autoimmune hemolytic anemia, Autoimmune thrombocytopenia |
| Endocrine glands | Type I diabetes mellitus, Hashimoto's thyroiditis |
| Gastrointestinal system | Ulcerative Colitis, Crohn's Disease, Autoimmune Hepatis |
| Skin | Psoriasis, Leukemia, Pamphia |
Rheumatology specializes in systematic autoimmune diseases (multi-organ attack), the main ones being:
| Joint Damage (Arthritis) | Rheumatoid arthritis, Psoriatic arthritis, Axial spondyloarthritis, Juvenile idiopathic arthritis |
| Muscle - skin infection | Polymyositis, Dermatomyositis |
| Salivary and exocrine gland damage | Sjogren's syndrome |
| Skin and internal organ damage | Systemic erythematosus, systemic scleroderma |
| Vaginal Attacks (arteries and veins) |
Crohn's arteritis, Wegener's granulomatosis syndrome, Adamantiadis-Behcet's disease
Arthritis Takayasu, Kawasaki Disease
|
| Self-inflammatory diseases | Still's disease |
How serious are the autoimmune diseases?
In earlier times, when many were not even known about the etiology and pathophysiology (how to say in which cause the tissue destruction) of these diseases, and thus the range and effectiveness of drugs administered was limited, indeed, some of them may have poor outcome, particularly if they interfere with vital organs such as e.g. systemic lupus erythematosus with renal insult certain vasculitides, etc. Furthermore, other autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or Agkylopoiiti or spondylarthritis, can cause permanent and severe deformities of the joints and spine respectively and corresponding disability to those suffering therefrom. The side effects of current treatments, which most often included chronic use of very high doses of cortisone can in turn be opened new vicious cycle of serious problems for the patient (osteoporosis with fractures, hormonal and metabolic disorders, heart problems, etc.). In the last course decades of systematic research in basic science level, our knowledge of these diseases have multiplied at an impressive rate, and thus the treatments that resulted is now private ac More effective, with the least possible side effects for the human body. So few are now the cases of those who can only treat not to have full and dramatic response, while most sufferers usually live a normal and creative life.
Are there cures that cause complete healing?
Autoimmune diseases, for the most part, are characterized by chronicity. It does not look like an infection that will "pass" after taking our antibiotic for a few days. Usually, long-term treatment is needed to keep the disease in "recession" (sleeping) to limit tissue damage to a minimum. Another feature of these diseases is that they experience periods of recession and exacerbation, many times and without having any specific causative factor. Therefore, there should be close co-operation between the patient and the rheumatologist, in order to closely monitor and adjust the treatment whenever necessary.
Autoimmune rheumatic diseases
Frequently asked questions and their answers
Nearchus 18 | Chania
Telephone: 2821008940
Mobile: 6973356790



